Cryptocurrency refers to a form of digital currency that exists solely online, with Bitcoin being widely recognized as a prominent example. Similar to traditional currencies, individuals engage in buying and selling cryptocurrencies, considering them as valuable assets that have the potential to appreciate in value over time.
It is vital to understand that utilizing or transferring cryptocurrency can result in tax implications.
It is crucial to comprehend the tax implications associated with digital assets as it aids in preventing unforeseen expenses and guarantees adherence to legal requirements while managing them.
What are the key aspects of Cryptocurrency Transfers?
Transferring Crypto Between Wallets
Transferring cryptocurrency between wallets means moving your digital money from one place to another. Just like you might send money from one bank account to another, you can send cryptocurrency from your wallet to someone else’s or another wallet you own.
Similar to an email address, each wallet possesses a distinct address that ensures secure sending and receiving of cryptocurrencies.
Types of Wallets
You have various options for storing your cryptocurrencies, as there are multiple types of wallets available.
- Hot Wallets: These wallets are connected to the internet, making it easy to access and use your crypto. They are convenient for everyday transactions but may need to be more secure because they can be vulnerable to hackers.
- Cold Wallets: These wallets are not connected to the internet, which makes them very secure. They are ideal for storing large amounts of cryptocurrency that you don’t plan to use often. Examples include hardware wallets and paper wallets.
- Exchanges: These are platforms where you can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies. While exchanges can hold your crypto, transferring your funds to a private wallet is generally safer after trading.
Purpose of Transfers
People transfer cryptocurrencies for different reasons.
- Personal Transfers: You might send crypto to friends or family as a gift or for splitting costs.
- Trading: Many people transfer their cryptocurrencies to different wallets to buy or sell them on various exchanges, hoping to make a profit.
- Gifting: Transferring crypto can also be a unique way to give a gift, just like giving cash or a gift card.
What are Capital Gains Taxes in Crypto?
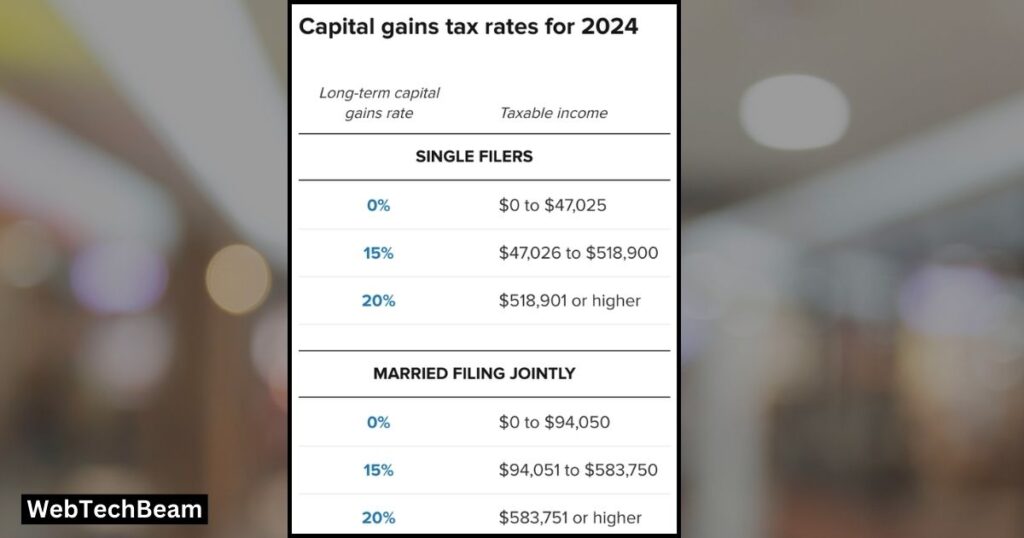
If you decide to sell or trade cryptocurrency, it is possible that you will be required to pay capital gains tax on any earnings. Capital gains are determined by the difference between the amount you initially invested in the cryptocurrency (known as the cost basis) and the amount you receive when you sell or exchange it. If the selling price exceeds your purchase price, the surplus is considered a capital gain. However, if you sell it for a lower price, you may experience a capital loss, which can be utilized to counterbalance other gains in your tax returns.
Keeping a record of every transaction is crucial, encompassing dates, amounts, and sale values. This data is essential for accurately reporting gains or losses during tax filing. As tax regulations differ across countries, it is advisable to review local laws or seek guidance from a tax expert to ensure compliance.
Taxable Events Explained
Definition of a Taxable Event
A taxable event refers to any transaction or activity that can lead to tax liabilities. Within the realm of cryptocurrency, a taxable event arises when you sell, exchange, or utilize your digital assets in a manner that generates either a gain or a loss.
If you purchase Bitcoin for $1,000 and subsequently sell it for $1,500, the act of selling becomes subject to taxation as you have gained a profit of $500.
Alternatively, if you were to sell it for $800, you would incur a loss that could potentially impact your tax obligations as well.
IRS Guidelines on Cryptocurrency Taxation
The IRS, or Internal Revenue Service, is the agency that collects taxes in the United States and has specific guidelines for how cryptocurrencies are taxed. According to these guidelines:
- Recognition of Gains or Losses: When you engage in a taxable event, you need to recognize the gains or losses. You must report how much money you made or lost when selling or exchanging cryptocurrency. This is important for correctly calculating your tax liability.
- Importance of Fair Market Value: The fair market value is the price your cryptocurrency would sell for on the open market. When you sell, trade, or otherwise use your cryptocurrency, you must determine its fair market value at that time. This value helps you determine your profit or loss, which will be used for reporting to the IRS.
To effectively handle cryptocurrency activities and fulfill tax obligations, it is essential to comprehend the associated terms and regulations. Maintaining precise transaction records will significantly facilitate the entire process.
When Sending Crypto is Taxable?

Selecting a Wallet Scenario
Sending cryptocurrency, whether from an exchange to your personal wallet or between your own wallets, can result in taxable situations. However, the initial purchase of Bitcoin from an exchange and subsequent transfer to your individual wallet is not subject to taxation.
Nevertheless, if you decide to sell or trade your Bitcoin for another asset such as cash or a different cryptocurrency in the future, it is possible that you will be liable to pay taxes on any gains you have obtained.
Cryptocurrency as Compensation or Payment
On occasion, individuals may receive cryptocurrency as compensation for their goods or services. If you opt to receive Bitcoin instead of traditional currency for work, it is important to note that this qualifies as taxable income. Similar to a standard paycheck, you are required to report the value of the Bitcoin received on the day of receipt as income.
Gifting Crypto Above IRS Exemption Limits
Giving cryptocurrency as a gift may also incur tax obligations. In the United States, the IRS permits individuals to give gifts up to a specific annual limit without incurring any tax liabilities, referred to as the annual gift tax exclusion.
Starting from 2023, the set limit stands at $17,000. In the event that you give cryptocurrency valued beyond this threshold to another individual, it may be necessary to declare it and potentially be subjected to taxes on the surplus amount.
Example:
Let’s say you purchase Bitcoin for $1,000, and at a later point, when its value reaches $20,000, you decide to give it as a gift to a friend. As the value of the gift surpasses the annual limit, you are required to report this on your tax return. Additionally, there is a possibility that you might owe taxes on the profit gained from this transaction.
When Sending Crypto is Not Taxable?

There are instances where sending cryptocurrency does not create any tax liabilities. Here are a few common scenarios:
Transfers Between Wallets Owned by the Same Individual
Transferring cryptocurrency between your own wallets does not trigger a taxable event as you are simply relocating your assets rather than selling or trading them.
Sending Crypto as a Gift Below the Exemption Threshold
If you give cryptocurrency as a gift and its value falls below the annual gift tax exclusion limit, you are not required to pay taxes. For example, if you give someone a gift of a Bitcoin worth $10,000 and the yearly limit is $17,000, this gift would be exempt from taxation.
Intra-Wallet Transfers Not Involving Sold Assets
Transferring cryptocurrency between wallets without converting it into cash or another cryptocurrency is not considered a taxable event. It is merely a process of relocating your assets.
Example:
If you possess $1,000 worth of Ethereum in Wallet A and transfer it to Wallet B, this transaction is not subject to taxation. However, if you eventually choose to sell the Ethereum for $1,500, you are only required to declare the resulting gain for tax purposes.
You can also explore What is a Certified Crypto Trader?
Remember to keep good records.

Maintaining precise records of your cryptocurrency transactions holds significant importance as it enables you to monitor your profits and losses, simplifying the process of reporting your taxes. In case you encounter inquiries from the IRS or any other tax authority, having comprehensive records can serve as evidence and support your position.
Having good record-keeping skills allows you to effectively manage your investments and gain a clear understanding of the performance of your cryptocurrency over a period of time.
What Records to Keep?
Staying organized would be easier if you retained important details about your transactions.
- Dates: Note when you bought, sold, or transferred your cryptocurrency.
- Amounts: Record how much cryptocurrency you purchased or sold and its value in cash at that time.
- Wallet Addresses: Write down the addresses of the wallets involved in each transaction. This helps you keep track of where your crypto is stored.
You can ensure your preparedness for tax season and prevent future complications by maintaining these records.
Conclusion
It is essential for individuals who engage in purchasing, selling, or possessing digital currencies to comprehend the taxation rules applicable to cryptocurrencies. It is important to bear in mind that specific activities such as selling, trading, or receiving crypto as payment can result in taxable events. Conversely, straightforward transfers between wallets typically do not have tax implications.
To simplify tax time, it is advisable to maintain thorough transaction records. If you find your circumstances complex or uncertain, seeking advice from a tax expert is recommended. They can assist you with the specifics and ensure your compliance with IRS regulations.
Being well-informed and prepared can help you avoid unforeseen tax responsibilities, potentially saving you money!
Common Queries about Crypto Wallet Transfer and Taxes
Are wallet-to-wallet transactions taxable?
Transferring cryptocurrency between your own wallets does not trigger any tax obligations as it does not involve a taxable event. It is merely a transfer of your assets without a sale or exchange, hence you are not required to report any taxes for that transaction.
Is there a fee for sending crypto to another wallet?
When transferring cryptocurrency between wallets on blockchain networks, a transaction fee, commonly referred to as “gas,” is typically imposed. This fee serves as a payment to the network for processing and verifying your transaction. It is crucial to take these fees into account when conducting any transfers.
Is transferring crypto to another exchange a taxable event?
Generally, the act of transferring cryptocurrency between exchanges is not subject to taxation. However, tax implications may arise if you choose to sell the crypto or convert it into a different asset either during or after the transfer. It is important to note that solely transferring your crypto between exchanges does not activate any tax obligations.
Is it taxable to trade one crypto for another?
When you trade one cryptocurrency for another, it is regarded as a taxable event by the IRS. This implies that you must disclose any profits or losses resulting from the transaction, calculated according to the cryptocurrencies’ fair market value at the moment of the exchange.
Do I have to pay taxes on cryptocurrency earned from mining?
When you earn cryptocurrency through mining, it is important to note that it is taxable income. You are required to report the fair market value of the cryptocurrency as income upon receipt.
Are there different tax implications for long-term vs. short-term cryptocurrency holdings?
Your tax obligations can be significantly influenced by the duration of your holdings. Typically, long-term holdings (assets held for more than a year) are subject to a lower capital gains tax rate, while short-term holdings (assets held for a year or less) are taxed as ordinary income, potentially at a higher rate.
Do Crypto Wallets Report to the IRS?
Cryptocurrency wallets do not automatically share transaction details with the IRS. Nevertheless, it is your obligation to monitor and disclose your transactions when filing your taxes. It is crucial to be aware of your earnings and expenses, as the IRS requires you to report your cryptocurrency income as well as any profits obtained from sales or trades.
Is Sending Crypto to Another Wallet Taxable? – Web Tech Beam 2024 Guide

